Paracentesis, Ascitic Tapping Procedure - Indications & Cost
PACE hospitals is one of the Best Hospital for Paracentesis procedure (Abdominal Fluid Removal) in Hyderabad, India. The Department of Gastroenterology is equipped with state-of-the-art facilities and next generation image-guided therapy platform to cater precise screening to carry out the evidence based abdominal paracentesis procedure to rule out any complications.
Our team of the best medical gastroenterologists and surgical gastroenterologist are well versed in the management of the severe and critical cases of ascites tapping with high success rate.
Request an appointment for Paracentesis (abdominal or ascitic fluid tapping)
Paracentesis (Ascitic fluid tapping) appointment
Thank you for contacting us. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 8977889778
Regards,
Pace Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Thank you for contacting us. We will get back to you as soon as possible. Kindly save these contact details in your contacts to receive calls and messages:-
Appointment Desk: 04048486868
Whatsapp: 8977889778
Regards,
Pace Hospitals
Hitech City and Madinaguda
Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
-
Quick Links
State-of-the-art advanced OT with 3D HD laparoscopic and laser equipment
Team of the best paracentesis doctor with 30+ years of expertise
Cost-effective treatment with 99.9% success rate
All insurance accepted with No-cost EMI option
What is Paracentesis procedure?
Paracentesis definition
Paracentesis, also known as ascitic tap or abdominal tapping, is a procedure that is mainly performed to drain the excess fluid from the abdominal cavity for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Paracentesis procedure, also known as abdominal or ascitic fluid tapping, is used for both therapeutic and diagnostic purposes to extract a small sample of or drain ascitic fluid. Ascitic fluid is drawn out of the peritoneal cavity using a needle or catheter. Ascites is the term used for excessive fluid in the abdomen. Usually, the abdominal cavity doesn't contain any fluid. The drained fluid can be tested for infections or cancers, as well as for determining the cause of ascites.
Paracentesis meaning
“Paracentesis” is the Greek word in which “para” refers to the structures adjacent to the specific organs or parts in the body, whereas “centesis” refers to the puncture. In medical terminology, paracentesis is the word that is literally used to puncture beside or adjacent to the abdomen to remove the excess fluid.
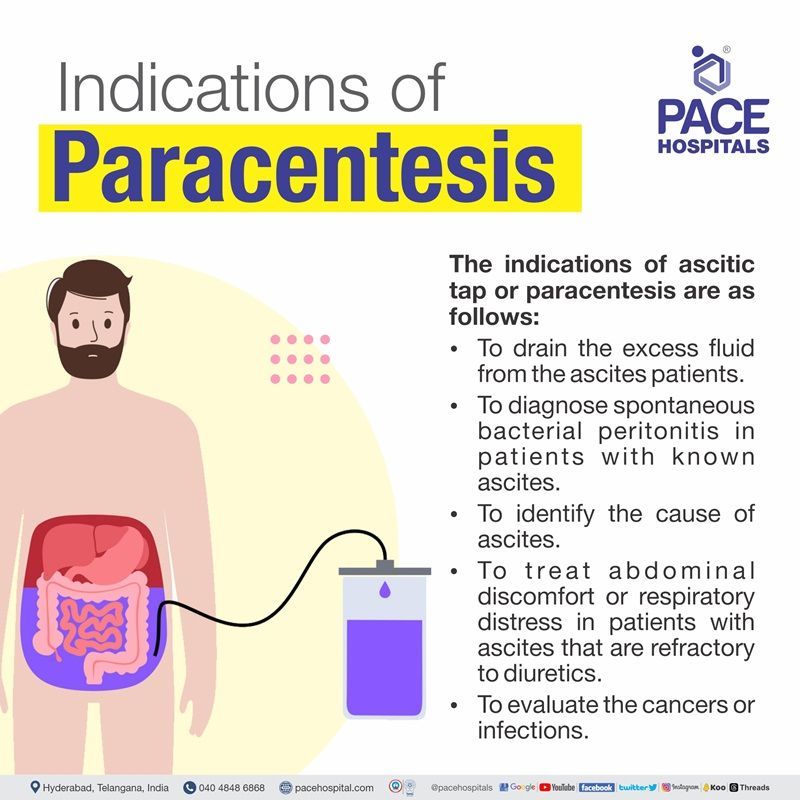
Paracentesis indications
The indications of ascitic tap or paracentesis are as follows:
- To drain the excess fluid from the ascites patients.
- To diagnose spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in patients with known ascites.
- To identify the cause of ascites.
- To treat abdominal discomfort or respiratory distress in patients with ascites that are refractory to diuretics.
- To evaluate the cancers or infections.
Paracentesis contraindications
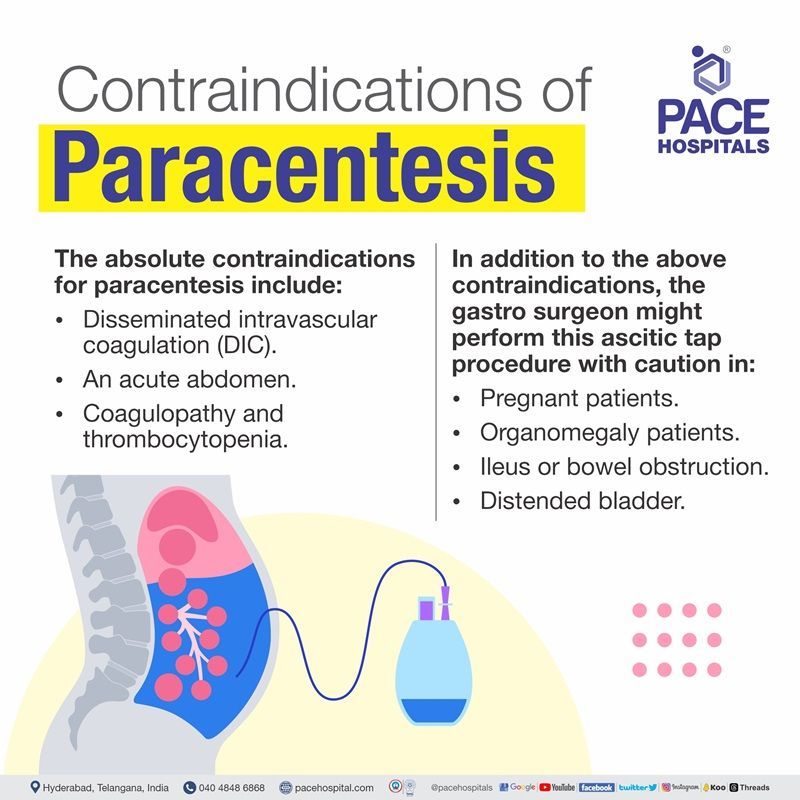
Some absolute contraindications for ascitic tapping include:
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC): DIC is a rare and serious condition that causes abnormal blood clotting.
- An acute abdomen: An acute abdomen is a condition that is usually present with a sudden onset of abdominal pain, nausea, or vomiting.
- Coagulopathy and thrombocytopenia: Although Coagulopathy (bleeding disorder) and thrombocytopenia (decreased platelet count) are not absolute contraindications, the incidence of bleeding complications from this ascitic tap procedure has been shown to be very low.
In addition to the above contraindications, the gastro surgeon might perform this ascitic tap procedure with caution in:
- Pregnant patients
- Organomegaly patients
- Ileus or bowel obstruction
- Distended bladder
Types of paracentesis or ascitic tap procedures
Paracentesis, or ascitic fluid tapping procedure, is mainly of two types:
- Diagnostic paracentesis or diagnostic ascitic tap: This method is usually performed to drain a small amount of fluid from the abdomen in order to test it for infections, cancer, or other abnormalities. It plays a major role in aspects of diagnosis.
- Therapeutic paracentesis or therapeutic ascitic tap: This approach is usually preferred to drain large amounts of fluid from the abdomen in order to reduce intra-abdominal pressure, dyspnoea, and abdominal pain conditions. This procedure is used in a conventional method (insertion of needle or syringe into the abdomen under ultrasound guidance), as well as large-volume paracentesis (to remove excess fluid, typically more than 5 litres).

Considerations of the surgical gastroenterologist / interventional radiologist before the procedure
Prior to the abdominal paracentesis procedure, the surgeon might consider the following factors:
- Patient’s medical history: The patient's medical history, which includes any underlying illnesses, allergies, and drugs they are currently taking, must be communicated to the surgeon. So that the surgeon will be able to detect potential risks related to the procedure with the aid of this information.
- Patient’s coagulation status: Prior to performing a paracentesis, the surgeon determines the patient's coagulation status or capacity to clot blood. This is crucial because paracentesis may result in bleeding, particularly in those who currently have bleeding circumstances.
- Patient’s vital signs: Prior to performing a paracentesis, the surgeon will also take the patient's vital signs, which include haert rate, blood pressure, and breathing rate. This is essential to detect any possible issues that can arise during the procedure, such as hypotension (low blood pressure) or hypoxia (low blood oxygen levels).
- Cause of ascites: The reason behind the ascites will additionally have to be known by the surgeon. This holds significance as it will aid in identifying the most effective therapeutic strategy.
- Location of the ascites: Abdominal ultrasound will be performed to know the exact ascitic fluid tapping location by the surgeon.
Goals of a surgical gastroenterologist / interventional radiologist for performing paracentesis
The goals of the surgeon performing paracentesis are:
- To diagnose the cause of ascites.
- To remove the excess fluid from the abdomen (the goal is to treat and manage the associated conditions).
- To prevent complications from ascites and other related abnormalities.
- To improve the patient’s quality of life.
Who should perform paracentesis?
- An interventional radiologist or gastrosurgeon usually performs paracentesis. Well-trained clinicians in the hospitals also perform it.
Before the paracentesis - ascitic tap procedure
- Before going to the procedure, the surgeon takes the entire medical history, physical examination, diagnostic criteria, laboratory results, and blood test data.
- Further, based on the hospital guidelines, the patient or patient representatives are asked to sign in for consent.
- As per the surgical protocol, the patient is recommended to stop eating or drinking for a few hours prior to the procedure.
- Prior to the procedure, the patient is asked to empty the bladder. This protects the patient from bladder injury during the procedure. A Foley catheter is placed on the patient to drain out the urine during the procedure.
- An IV lining is placed on the patient in order to supply the fluids and medicines.
- During the paracentesis procedure
- Usually, paracentesis is performed in the surgeon’s room or treatment room in the hospital.
- It is done in the lateral decubitus or in the supine position. This paracentesis position makes the superficial veins and surgical scars more visible and also avoids the puncture of the inferior epigastric arteries.
- An ultrasound imaging method is used to guide this procedure and makes it easier for the provider to find out the ascitic tapping site of the belly area where the needle is to be inserted.
- A local anaesthesia or numbing gel is applied or injected at the site of ascitic tap where the needle is to be inserted, and then the needle is inserted at a 45-degree angle or with a z-tracking technique (z technique for ascitic tap).
- Then, the fluid is extracted with a syringe. The amount of fluid to be removed depends on the patient's condition (either a diagnostic or therapeutic approach).
- The surgeon might draw a small amount of fluid for the diagnostic tap, whereas to remove large amounts of fluid, the surgeon might attach the catheter between the needle and syringe to extract more fluid.
- Once the fluid drain is over, the needle and syringe with the catheter are removed, and pressure is placed on the puncture site in order to avoid bleeding or fluid leakage.
- A small bandage or dressing is placed at the ascites tapping site.
After the paracentesis - ascitic tap procedure
- The patient is moved to the recovery room after the procedure to rest. Prophylactic antibiotics and postoperative analgesics are given to the patient in order to reduce the pain.
- The patient is likely to be sent home after 2 to 3 hours of the procedure. The underwent procedure and the care to be taken for the patient are explained to the caretaker.
- The patient will be discharged with suggested antibiotics and pain medications that might be used for a few days, and regular follow-up dates will be given to the patient by the surgeon.
Treatment after the paracentesis - ascitic tap procedure
- This might vary based on the patient’s condition. There may be a chance of recurrent ascites, which might require this procedure to be done several times.
- Keen observation is needed for post-procedure infections and vital changes. Symptoms such as fever, chills, trouble breathing, pain, and bleeding might require immediate treatment.
- The patient might be suggested diuretics for a few days in order to increase urination and decrease the fluid buildup in abdomen.
- The surgeon might suggest some remedies and specific instructions for the patient to follow.
Success rate of paracentesis or ascitic tap procedure
The success rate of the procedure usually depends on the patient's condition and their response to the procedure. Current health conditions and other co-morbid conditions might influence the success rate of the paracentesis. However, ascitic tap has a high success rate in normal individuals. Here are some of the following case studies that demonstrate the success rates:
- In a study, a total of 282 patients were considered; out of those, 127 (45%) were male and 155 (55%) were female. They had 722 scans done on them after the paracentesis procedure. 127 patients (18%) did not receive an intervention. A total of 545 patients (78%) had procedures: 463 patients (85%) had therapeutic (high volume) paracentesis, while 82 patients (15%) had diagnostic aspirations. The majority of scans were done between 8:00 and 17:00. Four hours and twenty-one minutes was the average duration from patient assessment to diagnostic aspiration.
- Three unsuccessful surgeries (0.6%) and one case of iatrogenic peritonitis (0.2%) were seen among the complications; however, there was no substantial bleeding, intestinal perforation, or fatality in any of the participants.
According to an evidence-based study, there is a 94% high success rate among the patients who underwent the paracentesis procedure.
Risk populations for abdominal paracentesis procedure
Though paracentesis is a minor and safest procedure, there are some risk factors for paracentesis. The following populations are at risks in ascites tapping:
- Underlying comorbidities or medical conditions: Patients with underlying comorbidities might increase their risk of developing complications.
- Hypotension (low blood pressure) and hypovolemia (low plasma blood levels): Patients with low blood pressure and hypovolemia are at increased risk of developing dizziness and light-headedness due to a large amount of fluid drain. To counteract hypotension, a human albumin solution is recommended to the patient by the surgeon.
- Patients on anti-coagulants and with bleeding disorders: Though it is not an absolute factor, there might be a chance of significant bleeding in this case.
- Cirrhosis: Cirrhosis might increase the risk of complications.
- Infections: abdominal infections might increase the risk of developing infections at the site of the puncture.
- Poor nutrition: Poor nutrition might also increase the development of infections in ascitic patients.
- Regular smoking and alcohol intake: There might be a chance of developing an infection.
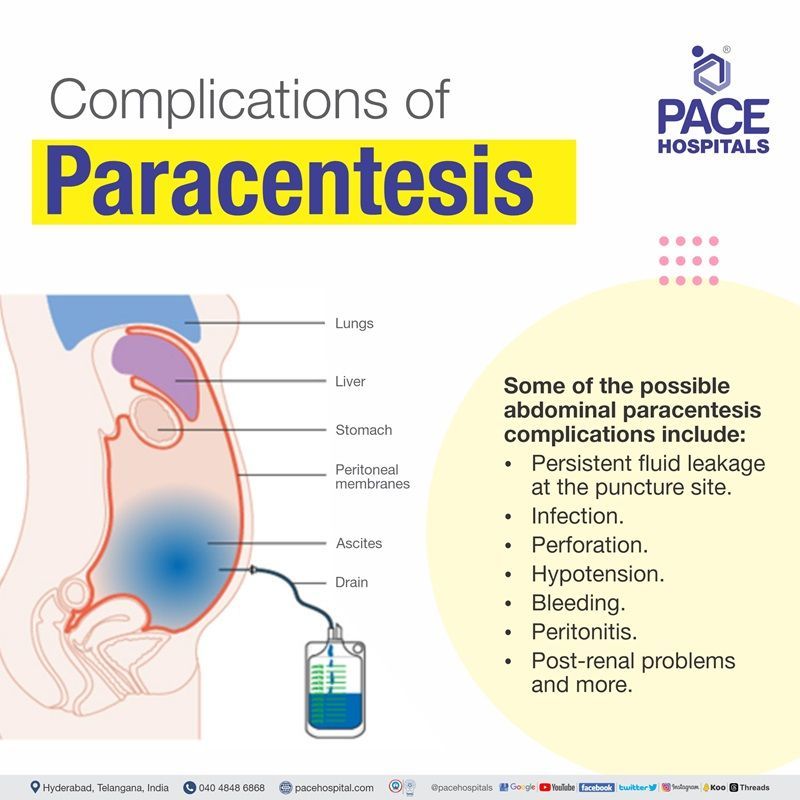
Complications of paracentesis - ascitic tap procedure
Though paracentesis is a minor and safest procedure, there might be a chance of developing some complications. Some of the possible abdominal paracentesis complications include:
- Persistent fluid leakage at the puncture site (Often, this can be fixed with a single skin suture).
- Infection (There might be a chance of developing an infection in some cases).
- Perforation (This is an extremely rare condition where an injury to the structures of the abdomen or surrounding blood vessels and viscera might take place).
- Hypotension (A large volume of ascites drainage might lead to hypotension in some circumstances; to avoid hypotension, albumin is frequently given after more than 5L of fluid has been removed).
- Bleeding (There might be a chance of developing bleeding in some cases).
- Abdominal wall hematomas
- Peritonitis (Inflammation of the abdominal lining)
- Post-renal problems and more.
Life after paracentesis or ascitic tap procedure
After paracentesis, most people have unremarkable lives. Following the procedure, most people are able to resume their regular activities in a day or two, there will be a moderate pain on that day at the puncture site which might be resolved and diminished itself. One may take a few steps, though, to make sure that rehabilitation goes well.
- Rest: After the surgery, avoid intense activity for a few days.
- Cold: To lessen discomfort and swelling at the puncture site, apply cold packs.
- Bandage: Use a bandage to keep the puncture site dry and clean.
- Keep an eye out for infection: Keep an eye out for symptoms of infection, such as fever, oedema, or redness.
- Follow-up: Schedule follow-up visits with your physician as necessary.
Paracentesis vs thoracentesis | Difference between paracentesis and thoracentesis
Paracentesis and thoracentesis are both are diagnostics and therapeutic procedures that involve draining fluid from the body. However, they differ in the location from which the fluid is drained.
| Parameters | Paracentesis | Thoracentesis |
|---|---|---|
| Also known as | Ascitic tap, ascites tapping, abdominal tapping , abdominal paracentesis procedure. | Thoracocentesis, pleural tap, needle thoracostomy, needle decompression |
| Indications | Performed to get a small sample of fluid or to drain ascitic fluid from the abdomen | Performed to remove air or fluid from the thoracic cavity. |
| Types | Diagnostic paracentesis procedure, therapeutic paracentesis procedure. | Diagnostic thoracentesis, therapeutic thoracentesis. |
| Contraindications | Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), An acute abdomen, Coagulopathy and thrombocytopenia | No absolute contraindications. |
| Patient position during surgery | Lateral decubitus or supine position | Supine or sitting position. |
| Complications | Persistent leakage, infection, perforation, hypotension, bleeding etc. | Bleeding, infection, hepatic and splenic puncture, retained intrathoracic catheter fragments, pulmonary oedema, etc. |
-
Is paracentesis a safe procedure?
Yes, paracentesis or ascitic tap procedure is a safe procedure. However, in some rare circumstances, it might cause complications such as leakage of ascitic fluid, infection, sudden fall of blood pressure, and injury to the surrounding structures.
-
Can fluid recur after paracentesis?
The paracentesis or ascitic tap procedure relieves symptoms in almost 90% of the patients who underwent it. In some cases, the fluid might build up again after a while, so the surgical gastroenterologist might reschedule again or suggest medicines if it is moderate ascites.
-
What causes ascites?
Ascites is a condition in which fluid builds up in the abdomen. This can cause a number of symptoms, including abdominal swelling, weight gain, and discomfort. There are a number of causes of ascites, including:
- Cirrhosis of the liver
- Heart failure
- Kidney failure
- Cancer
- Pancreatitis
- Tuberculosis
Treatment for ascites depends on the underlying cause. In some cases, the fluid can be removed with a procedure called paracentesis. In other cases, the underlying cause of the ascites will need to be treated.
-
Is paracentesis the same as ascitic tap?
Yes, paracentesis and ascitic tap are both the same procedures. Both terms refer to the insertion of a needle or catheter into the peritoneal cavity to remove ascitic fluid, which is the excess fluid that accumulates in the abdomen. The procedure can be performed for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes.
- Diagnostic paracentesis is performed to obtain a sample of ascitic fluid to determine the cause of the ascites, such as cirrhosis of the liver, heart failure, or cancer.
- Therapeutic paracentesis is performed to remove a large amount of ascitic fluid to relieve symptoms such as abdominal pain, shortness of breath, and difficulty walking. Removing excess fluid can also improve liver function and reduce the risk of complications.
Frequently asked questions on paracentesis or ascitic tap procedure
How much fluid is removed during paracentesis?
The removal of fluid depends on the procedure being performed on the patient. Usually, paracentesis or ascitic tap procedure will be done in two types: a diagnostic approach or a therapeutic approach. A small sample will be drawn for the diagnostic approach, whereas a large volume of fluid will be drawn for the therapeutic approach in order to treat the patient. Commonly, 1–5 litres of ascitic fluid will be drawn during the therapeutic approach; however, any volume removed greater than 5 litres is considered a large volume paracentesis (LVP).
Is paracentesis an effective procedure?
Studies have confirmed that paracentesis is an effective procedure compared to diuretic therapy due to less hospitalisation and better systemic and renal functioning preservation.
What is the success rate of a paracentesis?
Studies have shown that successful aspiration can be achieved in 94% of patients who undergo diagnostic paracentesis or ascitic tap procedure. Apart from this, a study was done on patients who were severely hospitalised with cirrhosis and ascites. It has been shown that out of 17711 admissions, 61% underwent paracentesis, and 24% achieved the best survival rate with reduced mortality. Finally, it was concluded that the mortality rate is lower in patients who underwent early paracentesis compared to later.
Why is albumin needed after paracentesis?
Usually, albumin administration will be done in patients who underwent large-volume fluid removal (more than 5 litres). Administering albumin can really prevent circulatory dysfunctions following large-volume paracentesis, renal failure, and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP). Finally, the gold standard of treatment for hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) is albumin, which is linked to vasoconstrictors.
What is the purpose of paracentesis?
Hepatologists (liver specialists) and surgical gastroenterologist usually recommend paracentesis for the treatment of ascites. It is also suggested for diagnostic purposes in order to find the illness and cause of the condition.
Does paracentesis require hospitalisation?
Paracentesis or ascitic tap procedure is a minor and safest procedure that will be done in and around 10-30 minutes in a doctor's room or treatment room. The patient might likely be sent home 1 to 2 hours after the procedure.
Is paracentesis painful?
The patient may feel a slight sting-like sensation from the numbing medicine or pressure during the needle insertion. If a large amount of fluid is drawn, the patient might feel dizzy or lightheaded.
Who performs ascitic tap or abdominal tapping?
An interventional radiologist or surgical gastroenterologist usually performs paracentesis or ascitic tap or abdominal tapping. Well-trained clinicians in the hospitals also perform it.
How much does a paracentesis cost in Hyderabad, Telangana?
Paracentesis cost in Hyderabad ranges varies from ₹ 5,000 to ₹ 7,000 (INR five thousand to seven thousand), this includes the cost of paracentesis or ascitic tap procedure procedure itself, as well as the cost of any anesthesia or medications that may be needed. However, price of paracentesis or ascitic tapping procedure in Hyderabad depends upon the multiple factors such as patient age, condition, and CGHS, ESI, EHS, insurance or corporate approvals for cashless facility.
What is the cost of paracentesis procedure in India?
Cost of paracentesis procedure in India, ranges vary from ₹ 4,800 to ₹ 8,000 (INR four thousand eight hundred to eight thousand). However, price of paracentesis or ascitic tap procedure in India can vary depending on the patient's condition and different private hospitals in different cities.
Our Locations
Subscribe to our newsletter and stay updated with the latest health information.
By clicking on subscribe now, you accept to receive communications from PACE Hospitals on email, SMS and Whatsapp.
Subscribe to PACE Hospitals News
Thank you for subscribing. Stay updated with the latest health information.
Oops, there was an error. Please try again submitting your details.
-

Payment in advance for treatment (Pay in Indian Rupees)
For Bank Transfer:-
Bank Name: HDFC
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.50200028705218
IFSC Code: HDFC0000545
Bank Name: STATE BANK OF INDIA
Company Name: Pace Hospitals
A/c No.62206858997
IFSC Code: SBIN0020299
Scan QR Code by Any Payment App (GPay, Paytm, Phonepe, BHIM, Bank Apps, Amazon, Airtel, Truecaller, Idea, Whatsapp etc)
Call us at 04048486868
ADDRESS
PACE Hospitals
Hitech City : Beside Avasa Hotel, Pillar No. 18, Hyderabad - 500081
Madinaguda: Mythri Nagar, Beside South India Shopping, Madinaguda, Hyderabad - 500050
QUICK LINKS
Disclaimer
General information on healthcare issues is made available by PACE Hospitals through this website (www.pacehospital.com), as well as its other websites and branded social media pages. The text, videos, illustrations, photographs, quoted information, and other materials found on these websites (here by collectively referred to as "Content") are offered for informational purposes only and is neither exhaustive nor complete. Prior to forming a decision in regard to your health, consult your doctor or any another healthcare professional. PACE Hospitals does not have an obligation to update or modify the "Content" or to explain or resolve any inconsistencies therein.
The "Content" from the website of PACE Hospitals or from its branded social media pages might include any adult explicit "Content" which is deemed exclusively medical or health-related and not otherwise. Publishing material or making references to specific sources, such as to any particular therapies, goods, drugs, practises, doctors, nurses, other healthcare professionals, diagnoses or procedures is done purely for informational purposes and does not reflect any endorsement by PACE Hospitals as such.

